

Standard Ambient Temperature and Pressure (SATP).Therefore, the volume of the gas of 12 kg is 9.60 m 3. The volume of the gas is molar volume multiple by the number of moles. The number of moles of nitrogen for a given weight ( W) is calculated as: The molar mass ( M) of the gas is 28 g mol −1. Calculate the volume of the gas if it behaves like an ideal gas? Source: History and Measurement of the Base and Derived Units, Steven A.
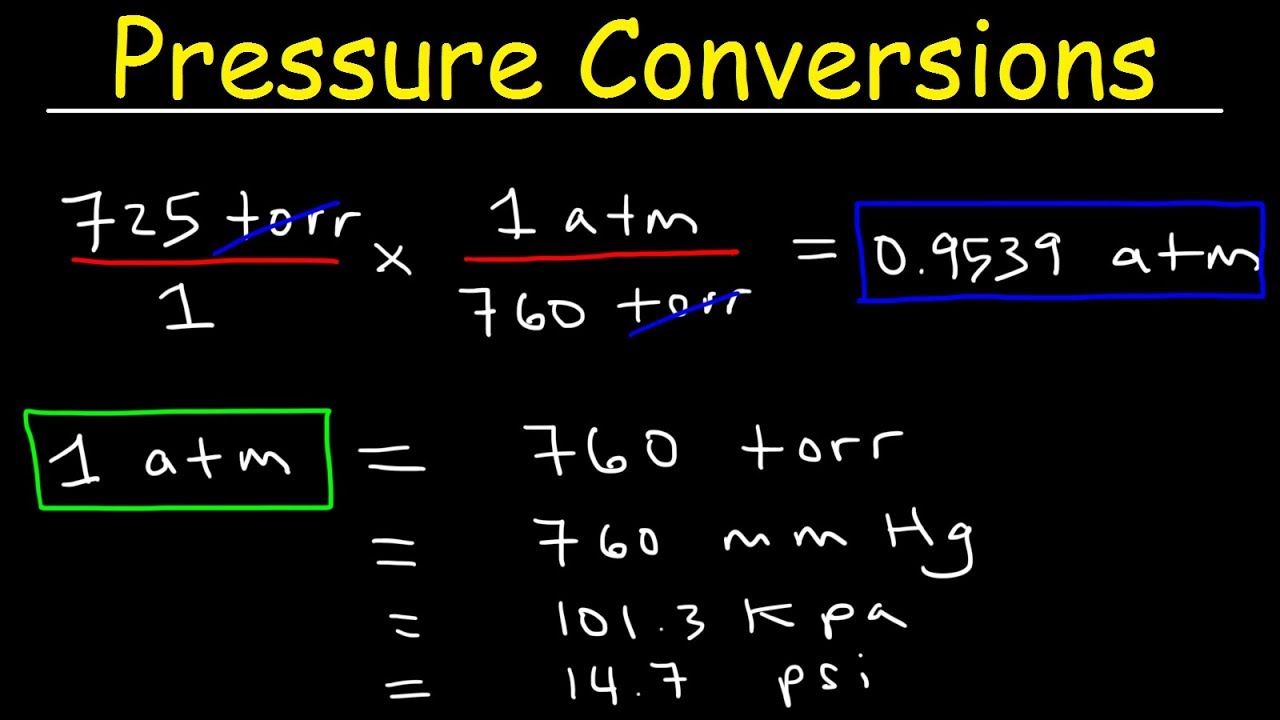
Note 2: T, Temperature P, Pressure RH, Relative Humidity V m, Molar Volume National Institute of Standards and Technology, NIST International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, IUPAC International Civil Aviation Organization, ICAO Euro-Asian Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification, EACSMC Occupational Safety and Health Administration, OSHA Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, OPEC Army Standard Metro, ASM Air Movement and Control Association, AMCA Federal Aviation Administration, FAA Common Refinery Standard Condition, CRSC Note 1: * indicates air is at 1.20 kg m −3. Comparison of Various Standard Conditions (Temperature and Pressure) with Molar Volume Institute The table below lists different standard conditions (pressure and temperature) adopted by different institutes. Temperature is 15 ℃, pressure is 1 atm, and relative humidity, 0 %. Standard Ambient Temperature and Pressure (SATP) There are many organisations who have developed their own standards based on their own needs. Where M is the molar mass of air ( M = 28.84 g mol −1).įor air at STP (IUPAC), Other Standard Conditions for Pressure and Temperature With the help of molar volume, we can also calculate the density of air. Where R is ideal gas constant, its value is 8.314 J K −1 mol −1. The molar volume V m of an ideal gas is defined as: A wrong assumption of standard conditions can lead to errors in calculations which can drastically affect outcomes.
#760 MMHG TO BAR PROFESSIONAL#
In professional work as well as in publications, it is very helpful to state standard conditions with volume (or volume dependent quantities) to avoid confusion. The same also applies to volume dependent quantities like molar volume, density, volumetric flow etc. As volume is a function of pressure and temperature, it is necessary to state the conditions (pressure and temperature) at which it is defined. The volume of gases is usually defined at standard conditions. But this definition of IUPAC is discontinued since 1982. Earlier (before 1982), IUPAC used to define standard temperature as 0 ℃ and standard pressure as 1 atm. While the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) defines standard temperature as 0 ℃ but standard pressure as 1 bar or 10 5 Pa. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an American physical sciences laboratory agency that defines standard temperature as 0 ℃ and standard pressure as 1 atm. One of such standards is STP (Standard Temperature and Pressure). Hence, to avoid such deviations we have adopted some standard conditions so that experiments all over the world are performed in similar laboratory conditions. This is because many scientific experiments, particularly of chemistry, are influenced by temperature and pressure. If the same experiment is conducted by him/her in Austin, where mean room temperature and pressure is 21 ℃ and 1.014 bar, the result of the experiments might significantly vary. Mean room temperature and pressure in London is 12 ℃ and 1.015 bar.

Let say a chemist in a laboratory is performing a chemical experiment in London. Standard Temperature and Pressure defined by IUPAC Standard temperature is 0 ℃ or 273.15 K or 32 ℉. Standard Temperature and Pressure defined by NIST


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
